Effective meetings are essential for any organization or team to collaborate, communicate, and make informed decisions. One key to ensuring that meetings run smoothly and achieve their objectives is to have a well-structured meeting agenda.
A meeting agenda helps keep discussions on track ensures that all necessary topics are covered, and makes the most of everyone’s time.
In this blog post, we’ll explore 16 meeting agenda examples and provide free templates to help you plan and run productive meetings.
Benefits of an Effective Meeting Agenda
In the hustle and bustle of today’s professional world, time is a precious commodity. Meetings, when not organized effectively, can often feel like a waste of time for both organizers and participants. However, having an effective meeting agenda can transform these gatherings into productive and efficient sessions. Let’s explore the numerous benefits of an effective meeting agenda:
Clarity and Focus on Meeting
An agenda serves as a roadmap for the meeting. It outlines the topics to be discussed and the goals to be achieved. This clarity ensures that participants understand the purpose of the meeting and can prepare accordingly. With a focused agenda, everyone stays on track, and discussions remain relevant to the meeting’s objectives.
Time Management
Time is money, and efficient meetings respect this fact. An agenda allocates specific time slots to each agenda item, preventing discussions from dragging on endlessly. It keeps the meeting on schedule, ensuring that it starts and ends on time. This time discipline is appreciated by all attendees, allowing them to plan their day effectively.
Preparation before Meeting
An agenda gives participants an opportunity to prepare in advance. They can gather necessary information, data, or reports, which leads to more meaningful contributions during the meeting. Prepared attendees are more likely to engage in discussions and provide valuable insights.
Participation and Engagement
With a clear agenda, everyone knows when it’s their turn to speak or contribute. This prevents interruptions and ensures that all voices are heard. Attendees are more likely to engage actively when they know what to expect, leading to more fruitful discussions and better decisions.
Efficient Decision making
Meetings are often called to make decisions. An agenda helps streamline the decision process by presenting the relevant information and guiding the discussion. This efficiency is particularly crucial in critical decision-making meetings, such as board meetings or project planning sessions.
Accountability
Agendas often include action items and follow-up tasks. This creates a sense of accountability among participants. They leave the meeting with a clear understanding of what they need to do next and by when. As a result, tasks are less likely to fall through the cracks.
Follow Up Meeting
After the meeting, the agenda serves as a reference point for meeting minutes or summaries. It helps ensure that all discussed topics are documented accurately. This documentation is essential for keeping everyone informed and for referencing past discussions in the future.
Flexibility
While agendas provide structure, they can also be flexible. If a pressing issue arises during the meeting, it can be added to the agenda for discussion. This ensures that important matters are addressed while maintaining the overall structure of the meeting.
Reduced Stress
Well-organized meetings with clear agendas are less stressful for both organizers and participants. Organizers can focus on facilitating the meeting, knowing that the agenda will guide the discussions. Participants can relax, knowing they won’t be caught off guard by unexpected topics or lengthy meetings.
Improved Reputation
Organizing and participating in effective meetings reflects positively on individuals and organizations. People appreciate the respect for their time and the commitment to achieving results. This can enhance the reputation of both meeting organizers and the organization as a whole.
How to Write a Meeting Agenda: 5 Key Steps
A well-structured meeting agenda is the backbone of a successful meeting. It sets the tone, provides direction, and ensures that the meeting achieves its objectives efficiently. Whether you’re organizing a team meeting, board meeting, or any other type of gathering, follow these five key steps to create an effective meeting agenda:
1. Define the Meeting’s Purpose and Objectives
Before you start drafting the agenda, clearly define the purpose and objectives of the meeting. Ask yourself:
- Why is this meeting necessary?
- What do you hope to accomplish during the meeting?
- What are the desired outcomes?
Understanding the meeting’s goals will guide you in selecting relevant agenda topics and ensuring that the meeting remains focused on its primary purpose.
2. Identify and Prioritize Agenda Topics
List all the topics that need to be addressed during the meeting. These topics can include updates, discussions, decisions, and action items. Once you have a comprehensive list, prioritize the items based on their importance and relevance to the meeting’s objectives.
Consider the following when prioritizing agenda topics:
Urgency: Are there pressing matters that require immediate attention?
Impact: How will discussing each topic contribute to achieving the meeting’s goals?
Time Constraints: Can all topics realistically be covered within the allocated meeting time?
It’s essential to strike a balance between addressing critical issues and ensuring the meeting doesn’t become overly long and exhausting.
3. Set a Realistic Timeframe
Assign specific time allocations for each agenda item. This step is crucial for time management during the meeting. Be realistic about the time needed for each topic, taking into account discussions, questions, and any presentations. Avoid overloading the agenda with too many items, as this can lead to rushed discussions and an unproductive meeting.
4. Create a Clear Agenda Structure
Organize the agenda in a logical and clear structure. A typical meeting agenda includes the following elements:
Meeting Title and Date: Clearly state the meeting’s purpose and the date it will be held.
Agenda Items: List each agenda item along with its allocated time.
Presenter or Facilitator: Assign a person responsible for leading each agenda item.
Materials and Preparation: Specify if participants need to review documents or prepare anything in advance.
Open Floor: Include a section for any additional topics or concerns that participants may want to address. This demonstrates openness to input from attendees.
5. Share the Agenda in Advance
Distribute the agenda to all participants well in advance of the meeting. This allows attendees to prepare, gather relevant information, and understand the meeting’s flow. Sharing the agenda beforehand also signals your commitment to running an organized and efficient meeting.
Additionally, consider sending out any supporting documents or materials related to the agenda items. This further facilitates preparation and informed participation.
By following these five key steps, you can create a well-structured meeting agenda that serves as a valuable tool for organizing and conducting productive meetings. Remember that a thoughtfully crafted agenda not only saves time but also enhances the overall effectiveness and satisfaction of meeting participants.
An Example Agenda for Your Team Meeting
Team meetings are a cornerstone of effective collaboration, communication, and project progress within any organization. To ensure that your team meetings are productive and well organized, it’s essential to have a clear and structured agenda. Below is an example of an agenda for a typical team meeting:
Team Meeting Agenda
Date: [Insert Date]
Time: [Insert Time]
Location: [Insert Location or Virtual Meeting Link]
Meeting Opening
- Welcome and Call to Order
- Brief Overview of Meeting Objectives
Roll Call and Attendance
- Confirm who is present and note any absent team members
Approval of Previous Meeting Minutes
Review and approval of minutes from the last meeting
Team Updates
- Brief updates from each team member on their current tasks and progress
- Highlight any achievements or milestones reached since the last meeting
Discussion of Current Projects
Project 1:
- Key updates and progress
- Challenges and roadblocks
- Required actions or decisions
Project 2 (Repeat the same structure for each ongoing project)
Upcoming Deadlines and Deliverables
- Review upcoming project deadlines and deliverables
- Ensure alignment and allocate responsibilities
Open Floor for Questions and Concerns
- Provide an opportunity for team members to ask questions or voice concerns
- Encourage open discussion and problem-solving
Action Items
- Summarize action items and responsibilities
- Assign due dates for tasks and clarify expectations
Next Meeting Date and Time
- Confirm the date and time of the next team meeting
- Note any changes or special topics for the upcoming meeting
Closing Remarks
- Recap key takeaways from the meeting
- Express appreciation for team members’ contributions
- End the meeting on a positive note
Adjournment
- Officially close the meeting
This example agenda serves as a template that you can adapt to your team’s specific needs and preferences.
- Some additional tips for effective team meetings:
- Stick to the allocated time for each agenda item to ensure the meeting stays on schedule.
- Encourage active participation and engagement from all team members.
- Consider rotating the role of meeting facilitator to distribute responsibility and promote leadership development.
- Share the agenda and any relevant documents with the team in advance to facilitate preparation.
Remember that the primary goal of a team meeting is to foster collaboration, share information, and address challenges constructively. An organized agenda is a valuable tool in achieving these objectives and ensuring that your team meetings are both efficient and productive.
Now that we understand the importance of a meeting agenda, let’s explore

16 meeting agenda examples you can use for different types of meetings:
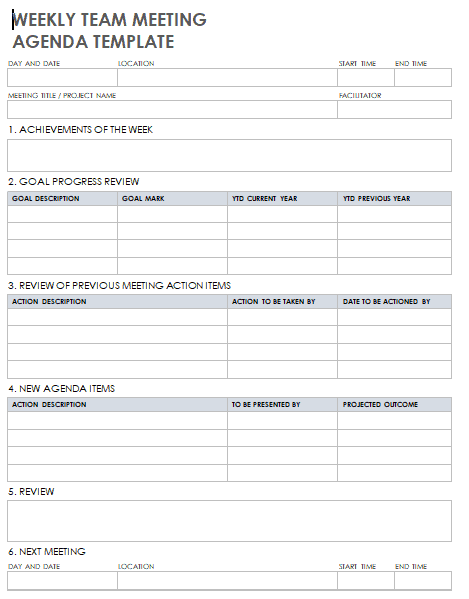
1. Weekly Team Meeting Agenda
Date and Time: [Insert Date and Time]
Attendance: Begin by confirming who is present and noting any absent team members, ensuring accountability.
Review Previous Meeting Minutes: Briefly revisit the minutes from the last meeting to recap discussions and action items.
Team Updates: Provide each team member with an opportunity to share updates on their tasks, progress, achievements, and challenges since the last meeting.
Discussion of Current Projects: Dedicate time to discuss the status of ongoing projects, address issues, and make decisions if needed.
Upcoming Deadlines: Review upcoming project deadlines and deliverables to ensure that everyone is aware of their commitments.
Open Floor for Questions and Concerns: Allow team members to ask questions or express concerns, fostering open communication and problem-solving.
Action Items: Summarize tasks and responsibilities assigned during the meeting, ensuring clarity on what needs to be done and by when.
Next Meeting Date and Time: Confirm the date and time of the next weekly team meeting, allowing participants to plan ahead.
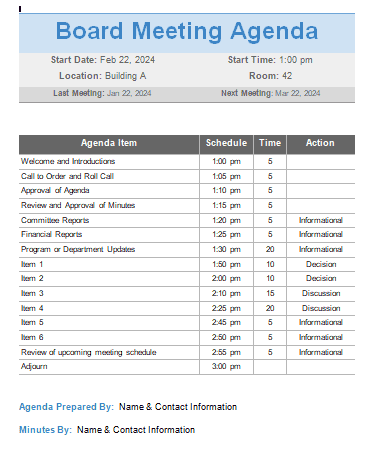
2. Board Meeting Agenda
Call to Order: The meeting begins formally with the chairperson or board president calling members to order.
Approval of Minutes from the Previous Meeting: Review and approve the minutes from the last board meeting, ensuring an accurate record.
Financial Report: Present and discuss the organization’s financial status, including income, expenses, budgets, and projections.
Committee Reports: Representatives from various committees provide updates on their respective areas, highlighting developments and recommendations.
Old Business: Discuss previously raised issues or matters that were tabled for further consideration, allowing the board to revisit unresolved topics.
New Business: Introduce and discuss new topics, proposals, or initiatives that require board attention and decision-making.
Guest Presentations: Allow guest speakers or experts to present relevant information or insights to the board.
Discussion and Decisions: Engage in in-depth discussions on agenda items, followed by decision-making, often involving voting on resolutions or actions.
Adjournment: Officially conclude the meeting, typically with a motion and vote, marking the meeting’s formal closure.
3. Project Kickoff Meeting Agenda
Introduction and Welcome: Start the meeting with a warm welcome to all participants, introducing key team members and stakeholders.
Project Overview: Provide an overview of the project’s purpose, goals, and high-level expectations, ensuring everyone understands its objectives.
Scope and Objectives: Discuss the project’s scope in detail, including what’s included and what’s not, and define clear objectives to align the team.
Roles and Responsibilities: Identify team members’ roles and responsibilities, promoting accountability and clarity within the team.
Project Timeline: Present the project’s timeline, including milestones, deadlines, and key phases, helping participants grasp the project’s timeframe.
Risk Assessment: Discuss potential risks and challenges, and outline strategies for risk mitigation and contingency plans.
Communication Plan: Explain the project’s communication strategy, defining how information will be shared, who is responsible for communication, and communication frequency.
Q&A: Allocate time for participants to ask questions and seek clarification, ensuring that all concerns are addressed.
Next Steps and Action Items: Summarize what needs to happen after the kickoff meeting, assigning responsibilities and setting deadlines to move the project forward.
4. Sales Team Meeting Agenda
Sales Metrics Review: Examine key sales metrics, such as revenue, conversion rates, and sales targets, to assess team performance.
Pipeline Update: Discuss the status of the sales pipeline, including leads, opportunities, and sales stages.
Discuss Sales Strategies: Review and discuss sales strategies, techniques, and tactics to improve sales performance.
Product Updates: Share information about product developments or changes that might impact the sales process.
Customer Feedback: Discuss customer feedback and insights gained from interactions, helping to refine sales approaches.
Obstacles and Challenges: Identify obstacles or challenges faced by the sales team and brainstorm solutions.
Sales Training: If necessary, allocate time for sales training sessions to enhance team skills and knowledge.
Open Forum for Ideas: Encourage team members to share ideas and suggestions for improving sales processes.
Sales Goals for the Next Period: Define sales targets and objectives for the upcoming period.
5. Training Workshop Agenda
Welcome and Introduction: Begin with a warm welcome and introduce the workshop’s objectives.
Agenda Review: Provide an overview of the workshop schedule and topics to be covered.
Presentation or Workshop Sessions: Conduct presentation sessions or hands-on workshops, addressing the workshop’s core content.
Group Activities: Facilitate interactive group activities or discussions to reinforce learning.
Breaks and Refreshments: Include scheduled breaks for participants to rest and recharge.
Q&A Sessions: Allocate time for participants to ask questions and seek clarification on workshop content.
Feedback and Evaluation: Gather feedback from participants to assess the workshop’s effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Closing Remarks: Summarize key takeaways, express appreciation, and conclude the workshop on a positive note.
6. Conference Call Meeting Agenda
Dialing Information: Provide participants with the necessary calling details and access codes.
Agenda Overview: Present a brief overview of the meeting’s agenda and objectives.
Updates and Reports: Share updates and reports relevant to the conference call’s purpose.
Discussion Topics: Address the main discussion topics or agenda items.
Q&A: Allow participants to ask questions and seek clarification.
Next Steps and Follow-up: Summarize action items and follow-up tasks, if applicable.
7. Monthly Review Meeting Agenda
Review of Monthly Goals: Examine the progress made toward achieving monthly goals and targets.
Performance Metrics: Analyze performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Accomplishments: Celebrate achievements and milestones reached during the month.
Challenges and Lessons Learned: Discuss challenges faced and lessons learned to improve future performance.
Action Items: Summarize action items and tasks to address in the coming month.
Upcoming Goals and Plans: Outline goals and plans for the upcoming month or period.
8. Nonprofit Board Meeting Agenda
Call to Order and Welcome: Begin by formally calling the meeting to order and welcoming attendees.
Approval of Agenda: Confirm and approve the meeting’s agenda.
Review of Previous Minutes: Review and approve the minutes from the last board meeting.
Committee Reports: Representatives from various committees provide updates.
Financial Report: Present the nonprofit organization’s financial status.
Old Business: Discuss unresolved matters from previous meetings.
New Business: Address new topics or initiatives that require board attention.
Guest Presentations: Allow guest speakers or experts to present relevant information.
Adjournment: Officially conclude the meeting.
9. Project Status Meeting Agenda
Project Updates: Provide updates on the project’s progress, accomplishments, and challenges.
Milestone Review: Review project milestones and their status.
Resource Allocation: Discuss resource allocation and ensure team members have what they need.
Issues and Roadblocks: Address any project-related issues or roadblocks.
Action Items: Summarize action items and tasks assigned during the meeting.
Next Steps: Outline the steps and tasks for the next phase of the project.
Closing Remarks: Conclude the meeting with any final remarks or acknowledgments.
10. Safety Committee Meeting Agenda
Safety Incidents Review: Discuss recent safety incidents or accidents.
Training Updates: Share updates on safety training programs and initiatives.
Safety Measures: Review and evaluate current safety measures and protocols.
Open Discussion on Safety Concerns: Allow members to voice safety concerns or suggestions.
Action Items: Summarize action items for improving safety measures.
Future Safety Goals: Set goals and plans for enhancing safety in the organization.
11. Product Development Meeting Agenda
Review of Product Roadmap: Discuss the product roadmap and its alignment with strategic goals.
Project Status: Provide updates on ongoing product development projects.
Market Research: Share findings from market research, customer feedback, and competitive analysis.
Competitor Analysis: Discuss insights gained from analyzing competitors.
Product Testing and Feedback: Present results from product testing and user feedback.
Next Steps: Outline the next steps in product development.
12. Marketing Strategy Meeting Agenda
Marketing Campaign Updates: Review the status and performance of ongoing marketing campaigns.
Social Media Strategy: Discuss strategies for social media marketing.
Content Calendar: Review and update the content calendar.
Analytics and KPIs: Analyze marketing analytics and key performance indicators.
Budget Allocation: Discuss the allocation of the marketing budget.
Next Marketing Initiatives: Outline upcoming marketing initiatives.
13. Client Meeting Agenda
Introduction and Welcome: Start with a warm welcome and introduction.
Client Updates: Provide updates on the client’s project or account.
Project Progress: Discuss the progress of ongoing projects.
Deliverables and Expectations: Review deliverables and set clear expectations.
Feedback and Concerns: Encourage clients to provide feedback or express concerns.
Next Steps and Action Items: Summarize action items and tasks for both parties.
14. Staff Training Meeting Agenda
Training Topic: Introduce the topic or theme of the training.
Presentation or Workshop: Conduct the main training presentation or workshop.
Hands-on Practice: Allow participants to apply what they’ve learned through hands-on activities.
Q&A: Address questions and provide clarification on the training content.
Feedback and Evaluation: Gather feedback to assess the effectiveness of the training.
Training Completion and Certification: Provide certificates or recognition for completing the training.
15. Agile Scrum Meeting Agenda
Sprint Review: Review the outcomes and progress of the current sprint.
Sprint Planning: Plan and prioritize tasks for the upcoming sprint.
Daily Stand-Up: Hold a brief daily standup meeting to discuss progress, obstacles, and goals for the day.
Issues and Blockers: Address any issues or blockers that may impede progress.
Task Assignment: Assign tasks to team members based on their skills and availability.
Sprint Retrospective: Reflect on the sprint’s performance and discuss areas for improvement.
16. Departmental Meeting Agenda
Department Updates: Provide updates on department-specific activities, projects, and achievements.
Project Status: Discuss the status of ongoing department projects.
Discussion on Department Goals: Review and discuss departmental goals and objectives.
Challenges and Solutions: Address any challenges faced by the department and brainstorm solutions.
Action Items: Summarize action items and tasks assigned during the meeting.
Upcoming Department Initiatives: Outline upcoming initiatives and projects within the department.
These detailed meeting agendas are designed to ensure that each meeting serves its intended purpose, whether it’s for team coordination, decision-making, training, or strategic planning.
**Best Meeting Management Software**
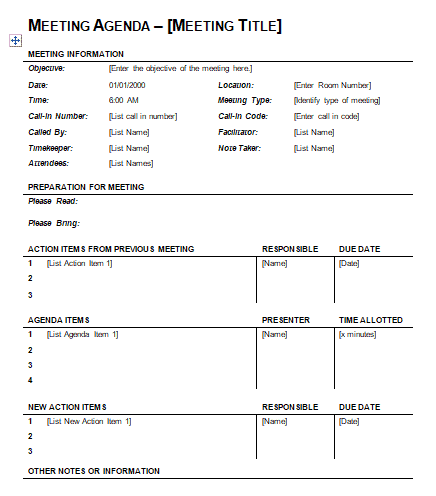
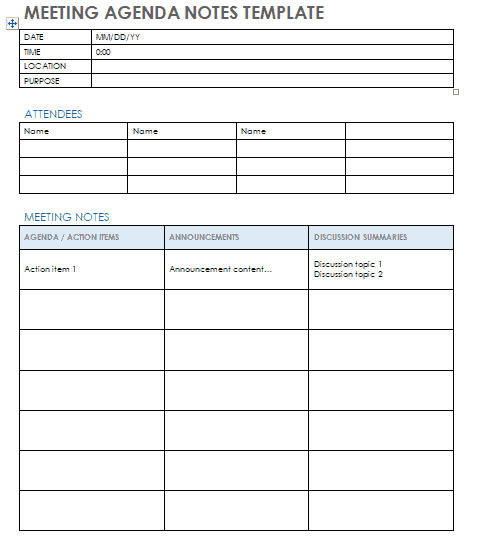
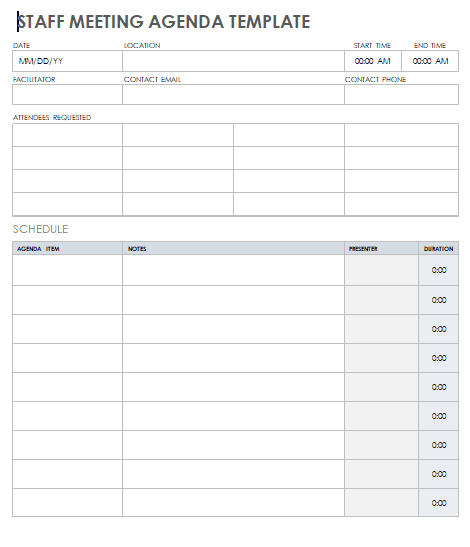
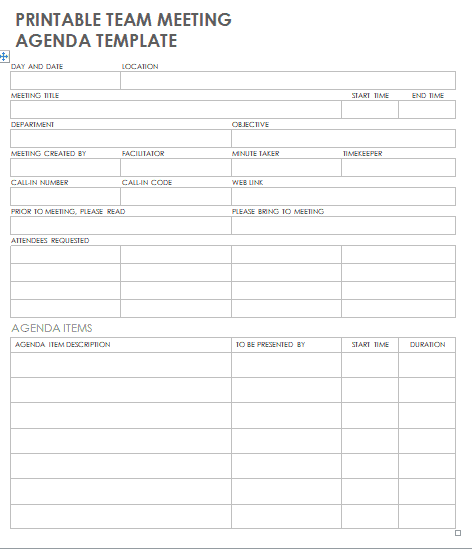
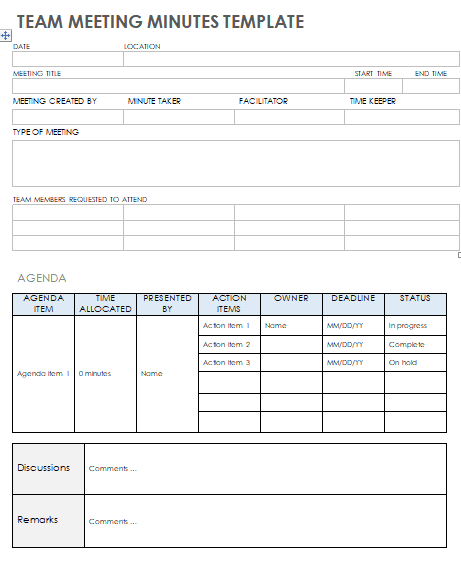
Some Free Meeting Agenda Template
You can download this template Docs file.